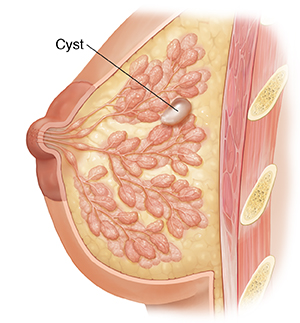
Breast cyst drainage (aspiration) is a procedure used to remove fluid from a breast cyst. A breast cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms in the breast tissue. You can have one or more cysts in one or both breasts.
Why breast cyst aspiration is done
Breast cyst aspiration may be done if you have a breast cyst that is large, persists, appears abnormal, or causes symptoms. This can include pain or soreness in the breast. The procedure may also be done if you have a breast cyst that keeps going away and coming back.
How breast cyst aspiration is done
Breast cyst drainage is a quick procedure. It may be done in a health care provider’s office, hospital, or radiology center. During the procedure:
-
The skin over the breast is cleaned.
-
The provider injects a medicine (local anesthetic) into the area. This helps prevent pain during the procedure.
-
When the area is numb, the provider puts a needle into the cyst. Then they drain the fluid from the cyst into the attached syringe. In some cases, they may use imaging methods such as ultrasound. These can help locate and guide the needle into the cyst before it is drained.
-
In most cases, a tiny tissue marker is placed where the procedure was done. This marker shows up on mammograms or other imaging tests. It marks the exact location if more treatment is needed. It also prevents retesting of benign lesions.
-
After the needle and syringe are removed, medical staff will put direct pressure on the injection site to help prevent bleeding. A bandage may then be placed over the site.
-
If needed, a sample of fluid from the cyst (cytology, a type of limited biopsy) is sent to a lab and studied under a microscope. This helps check for cancer and other problems that can happen in the breast.
Risks of breast cyst aspiration
-
Pain
-
Infection
-
Too much bruising
-
Bleeding or a collection of blood under the skin (hematoma)
-
Collapsed lung (very rare)
-
Return of the breast cyst
-
Need for more procedures, such as breast surgery to remove the cyst if it doesn't go away after aspiration
Featured in
Author: Yang, Sue
Online Medical Reviewer: Heather M Trevino BSN RNC
Online Medical Reviewer: Marianne Fraser MSN RN
Online Medical Reviewer: Rajadurai Samnishanth Researcher
Date Last Reviewed: 01/01/2025
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.